The United States international trade deficit in goods and services widened to $78.8 billion in July 2024, an increase from $73.0 billion in June. This rise was due to a $1.3 billion increase in exports to $266.6 billion and a $7.1 billion surge in imports to $345.4 billion. The goods deficit grew by $5.6 billion to $103.1 billion, while the services surplus decreased by $0.2 billion to $24.3 billion.
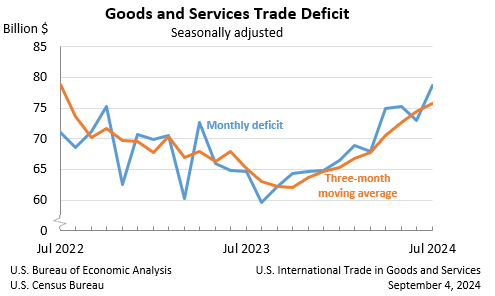
Year-to-date, the cumulative deficit rose by $36.2 billion, or 7.7 per cent, compared to the same period in 2023. Exports increased by $65.9 billion, or 3.7 per cent, and imports increased by $102.1 billion, or 4.5 per cent. The three-month moving average deficit also increased by $1.3 billion to $75.7 billion.
In July, the real goods deficit, adjusted for inflation, expanded by $6.3 billion to $97.6 billion. Real exports of goods decreased by $1.7 billion, while real imports rose by $4.6 billion. Revisions to earlier trade data showed minor adjustments.
The US recorded trade surpluses with several countries, including the Netherlands and Hong Kong, but faced significant deficits with China, the European Union (EU), and Mexico.
Attribution: US Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA)
Subediting: M. S. Salama


