German economy still in phase of ‘pronounced weakness’, to stagnate in ’25 – GCEE
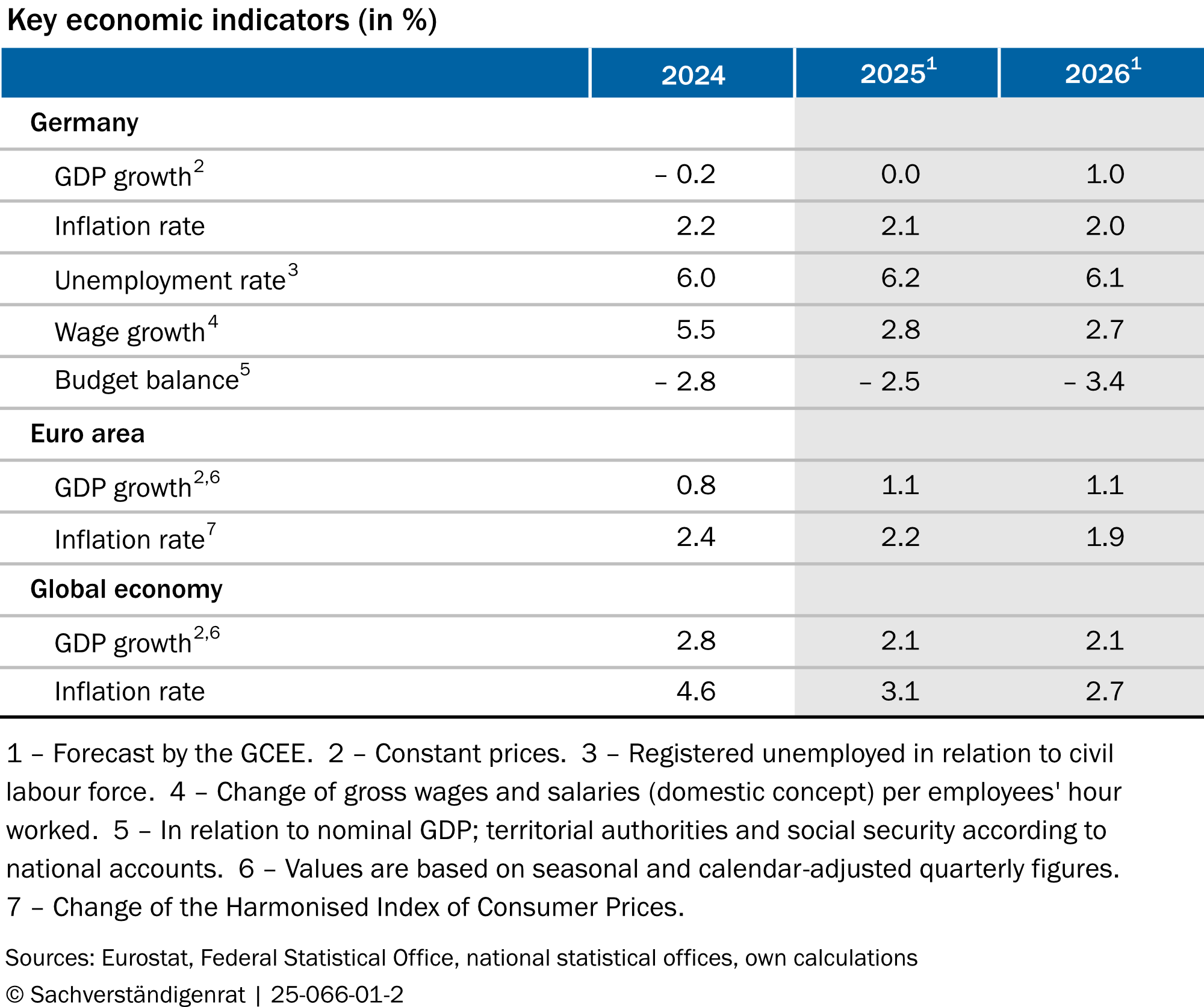
The German Council of Economic Experts (GCEE) said Wednesday that the German economy “is still in a phase of economic weakness” with GDP expected to stagnate this year and grow by only 1.0 per cent in 2026.
“The German economy is still in a phase of pronounced weakness. Bureaucratic requirements and long approval procedures are slowing down overall economic growth.” GCEE said in its Spring Report 2025.
“Structural change is accelerating and will also reach sectors and regions that have so far been economically strong. US President Donald Trump’s trade policy is jeopardising economic growth worldwide. The fiscal package offers opportunities for Germany to modernise its infrastructure and to return to a higher growth path.”
GCEE Chair Monika Schnitzer explained that the German economy in the near future “will be significantly influenced by two factors: US trade policy and the fiscal package,”
The US trade policy represents an additional burden on the already weak German exports.
“With a sharp and unpredictable rise in tariffs, German exports are likely to decline even further. From 2026, the funds provided by the fiscal package will entail positive effects on construction and investment in machinery and equipment as well as on government consumption.”
GCEE also said private consumption is expected to grow slightly more compared to 2025 as real disposable income will increase more strongly.
US trade policy places an additional burden on the already weak German exports. With a sharp and unpredictable rise in tariffs, German exports are likely to decline even further. From 2026, the funds provided by the fiscal package will entail positive effects on construction and investment in machinery and equipment as well as on government consumption. Private consumption is expected to grow slightly more compared to 2025 as real disposable income will increase more strongly. The GCEE expects that real gross domestic product (GDP) in Germany will stagnate this year (corresponding to a growth of 0.0 per cent) and increase by 1.0 per cent in 2026.
Consumer price inflation is projected to be 2.1 per cent on average in 2025 and fall slightly to 2.0 per cent in 2026.
“Although markets anticipate interest rate cuts, the inflation outlook remains highly uncertain. For instance, it is unclear whether ongoing trade conflicts will fuel or dampen inflation.” Veronika Grimm, council member, said.
“In addition, expansionary fiscal policies in Germany could raise inflation expectations, potentially prompting the ECB to favour a more restrictive monetary policy stance,”
Attribution: Amwal Al Ghad English